It’s been an interesting year in Google-land, with a number of large updates, including those in March, April and August.
Many have written at length and shared related data about all of these updates. In today’s post, I’ll cover in depth one aspect of the August update that hasn’t received much attention: brand authority.
I believe that one significant component of what Google did with the August update — increasing rankings for sites with general brand authority — was an adjustment to the impact of the March and April updates.
To be clear, the August update clearly had many different components that are also of critical importance. I’m calling out brand authority because it was not explicitly identified by other articles on the update.
I’ll go into this more deeply below, but I’ll begin with a brief recap of what others have said about the March, April and August updates. Feel free to skip ahead.
A brief recap of the March and April updates
I’m not going to repeat what’s already been said in the many excellent articles about these updates (though I link to some of them below). I will summarize some of the basics, then add some additional thoughts about what happened.
Here are some of the key quotes from Google on the update:
Per Google’s John Mueller in the Webmaster Central office-hours hangout on April 23:
The updates that we made are more around relevance, where we’re trying to figure out which sites [are] relevant for certain queries and not so much a matter of quality overall. That might be something where we just don’t think your site is exactly relevant for those specific queries. It doesn’t mean that it’s a bad site, it’s just not relevant for those specific queries … That’s something that I think happens to a lot of sites over time in that they might be really high-quality content, but over time [they’re] just not seen as relevant in the overall picture of the web.
Overall, there is a general consensus that the main components of this update were about how your content’s relevance is measured and Google’s adjustments around its understanding of user intent. This is consistent with statements from Google, as well as the data shared and analyzed by a variety of people in the industry.
Here are some of their analyses:
- Recap by Barry Schwartz on March 12, 2018
- Recap by Marie Haynes, last updated April 23, 2018
- Recap by Glenn Gabe on May 16, 2018 (Part One)
- Recap by Glenn Gabe on June 5, 2018 (Part Two)
My supplemental comments on the March and April updates
One aspect of the March and April updates that didn’t get much attention is the idea that the breadth and depth of a site’s content were considered as a ranking signal. Sites with large volumes of content that thoroughly and completely address a topic of interest did extremely well in these updates. Here is how I would characterize breadth and depth of content:
- Content created by true subject matter experts.
- Content created in high volume (from tens to hundreds of pieces of content per month).
- Content that addresses key topic areas both deeply and broadly. In other words, they address many subtopics that are important to users, not just the surface level of the topic area. This depth and breadth may be (and probably should be) accomplished across many articles.
- And, of course, content that isn’t sliced thinly for the sake of volume. Each of the different articles has a real reason to exist.
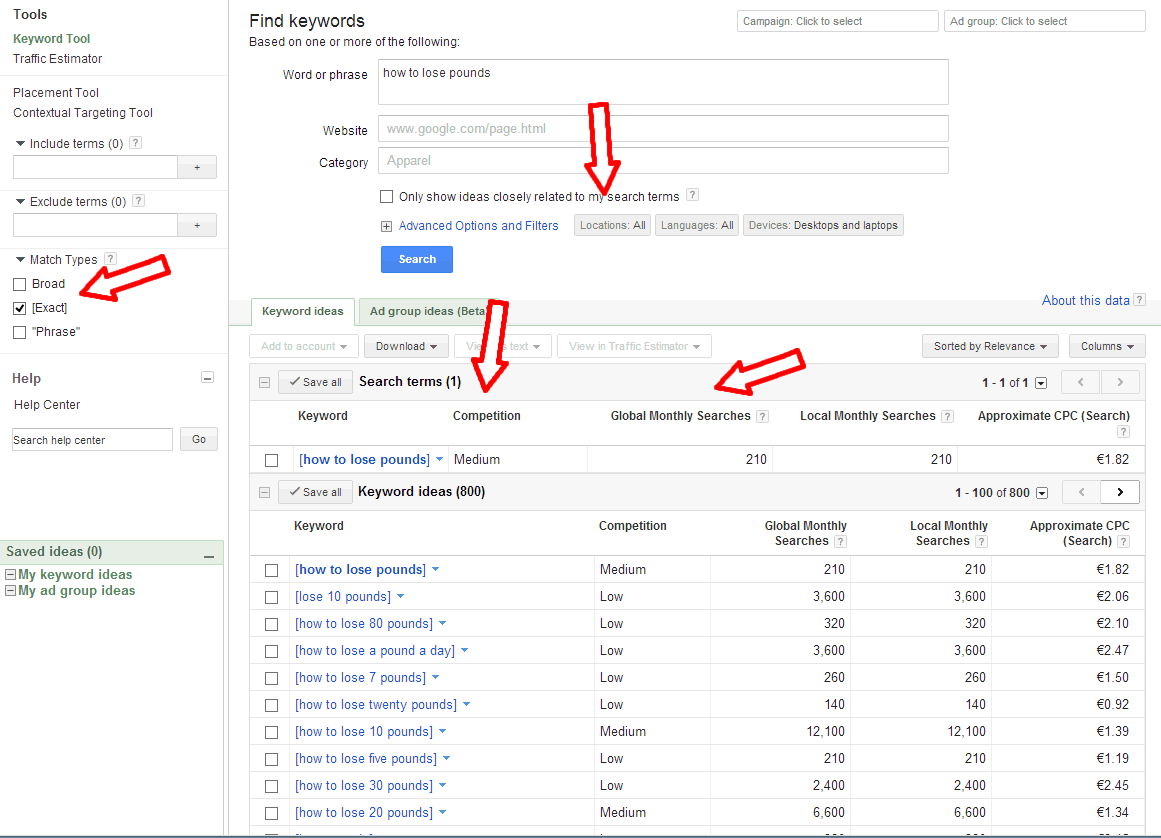
I saw many sites with these four characteristics experience a major uplift with the March and April updates. Here is an example of the Searchmetrics data through April for one of those sites:

As you can see, SEO visibility nearly doubled during the course of these updates. That’s a pretty serious set of gains! This is a phenomenon seen with many sites that follow this pattern of publishing quality content in volume. But, as noted, I do believe that a big key to this is the perceived depth and breadth of coverage of a topic.
To preserve anonymity, let me share what I mean with a fictitious example. Let’s say you want to be seen as an authority on replacing a kitchen sink. You might create a comprehensive article on the topic and include a companion video. That would be a great start. But perhaps some portion of your audience might be interested in one or more of these related topics:
- Disposing of the old sink.
- Installing a kitchen sink countertop.
- How to install kitchen sink plumbing.
- What type of caulk to use.
- How much it costs to replace a kitchen sink.
- What tools are needed for the job?
- Installing a garbage disposal with the sink.
- What would a plumber charge to install one?
- Changing a sink faucet.
- Special considerations for brass sinks.
- Special considerations for copper sinks.
I could keep going, but you get the idea.
A brief recap of the August update
People have called out many different aspects of this update. Some of the principal ones have been:
- Health-related sites being impacted more heavily, hence the “Medic” name Barry Schwartz gave to the update. However, it’s become clear that many different types of sites were impacted, not just health sites.
- An increased focus on expertise, authority and trust (E-A-T). In this context, authority tends to mean using subject matter expert writers, citing other authoritative research (including outbound links to same), managing your reputation online and so on.
- More speculation on aligning your content with user intent.
- Basic SEO factors like crawlability, avoiding thin content, mobile readiness and more.
There is not quite the same level of consensus that there was with the March and April updates, probably partly because Google made fewer statements specifically about it. In addition, I think it’s quite likely that between April and August, Google collected a lot of data on the March and April changes and decided to make a series of adjustments as a result. More on that in a minute.
Here are some of the recaps written about the August update:
- Recap by Barry Schwartz on August 8, 2018
- Recap by Barry Schwartz on August 9, 2018
- Recap by Ignite Visibility on August 14, 2018
- Recap by Marie Haynes, last updated on August 8, 2018 (Part Two)
Digging deeper into the August update
I already noted that when Google does any large-scale update, they continue to collect data on how the SERPs are performing, and they’re able to compare that with what they were seeing prior to a given update. Based on this, they can make adjustments to build upon the success of the earlier update and correct its weaknesses. It’s a process of continuous improvement.
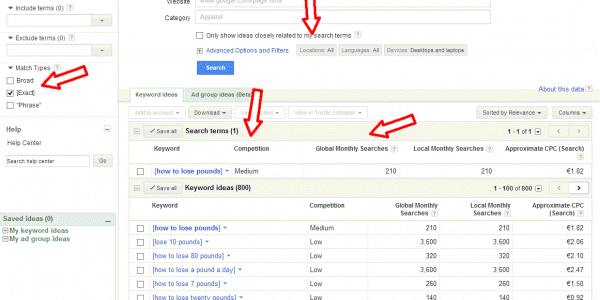
For example, here is the Searchmetrics data for one Fortune 100 retailer, showing a large drop to their traffic in April:

This site is for a very well-known brand, but it has fairly thin content on the e-commerce pages. The products are there, but there’s not much description or detail about them. And the site took a hit. However, they appear to have seen some level of recovery in the August update.
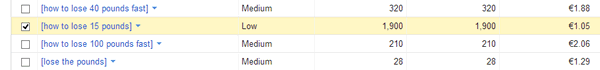
Here is a look at another site from a large, well-known brand through the same updates:
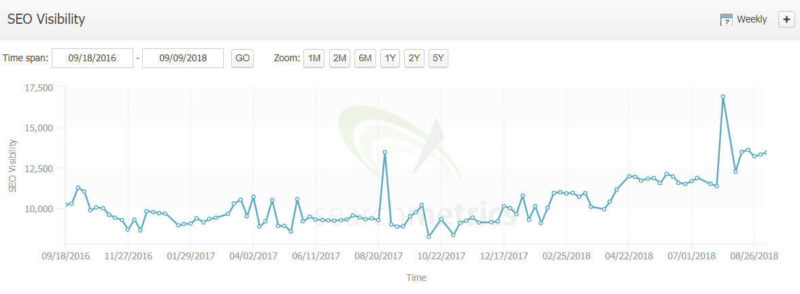
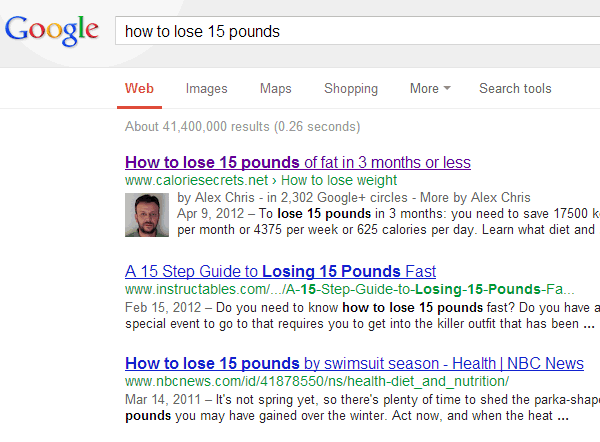
This site had the same problems with a lack of content on major e-commerce pages, and it took a substantial hit in the March and April time frame. However, it also recovered in the August update. So, I went looking for more of these. Here is an example from the travel industry:

Yes, another major brand with some content problems that sees a recovery in the August update. Here is yet another example of a prominent e-commerce site taking a hit in March and April but recovering in August:
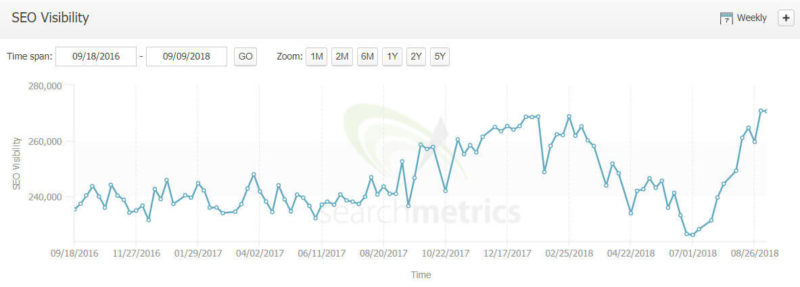
To try and figure out what was going on, I did an analysis of each of these sites (as well as several others). In each of the above cases, and in several others I looked at, it seemed like the March/April evaluation of the site’s relevance was hurt by a lack of good, in-depth content on their e-commerce pages.
Why did all these sites recover during the August update? Based on the data I’ve seen, my speculation is that the weight of brand authority signals was one of the things that was adjusted in the August update. When I talk about brand authority, I don’t mean authority in the E-A-T sense, but in the pure and simple strength and power of a brand. How does Google measure that? There are probably many components to it, including factors like links, mentions and overall user engagement with a brand.
Why should brand authority matter so much? Think of it from a user perspective for a moment. Users develop a strong affinity for brands. They learn to trust them, and they give them the benefit of the doubt. As related to this series of updates, it means they may prefer sites from prominent brands they trust, even though the content of those sites is materially weaker.
In addition, for curiosity’s sake, I also looked back at my example site that I shared earlier, the one that did really well with the March and April updates. How did it fare?
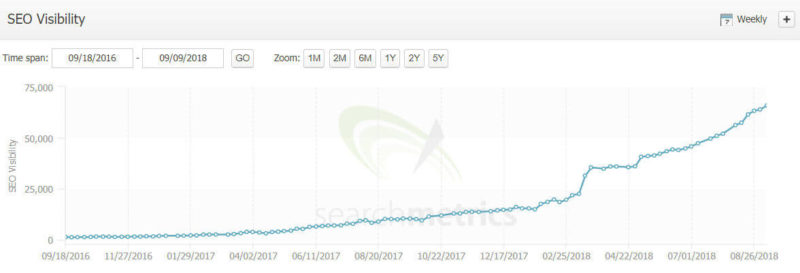
It kept on soaring upward! For that first example site, the depth and breadth of their content has kept them going strong.
Source:- Latest Google update