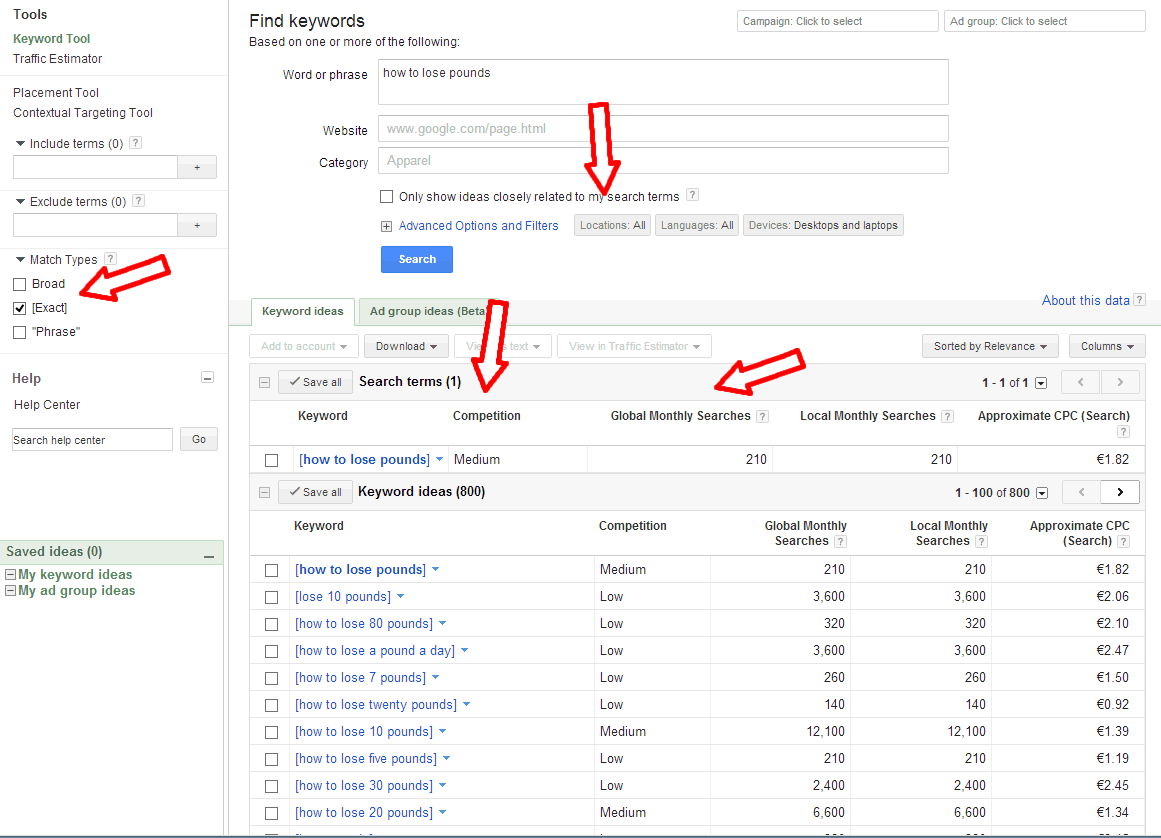
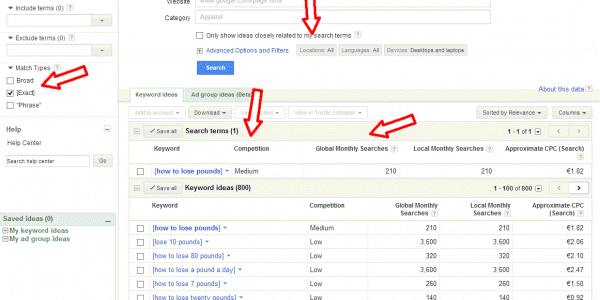
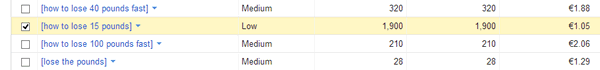
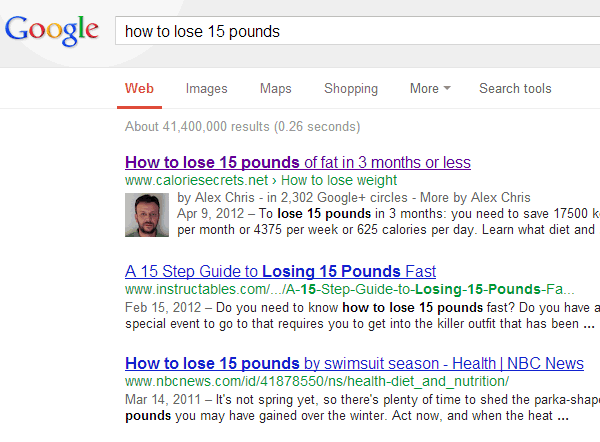
Each year, Google changes its search algorithm around 500–600 times. While most of these changes are minor, Google occasionally rolls out a "major" algorithmic update (such as Google Panda and Google Penguin) that affects search results in significant ways.
For search marketers, knowing the dates of these Google updates can help explain changes in rankings and organic website traffic and ultimately improve search engine optimization. Below, we’ve listed the major algorithmic changes that have had the biggest impact on search.
2018 Updates
"Medic" Core Update — August 1, 2018
Google confirmed a "broad core algorithm update," with wide reports of massive impact. It rolled out over the period of about a week, but peaked on August 1-2. This update seemed to disproportionately affect sites in the health and wellness vertical, although large-scale impact was seen in all verticals.
Chrome Security Warnings (Full Site) — July 24, 2018
After warning users of unsecured (non-HTTPS) forms months earlier, Chrome 68 began marking all non-HTTPS sites as "not secure." The changes rolled out on July 24, but rely on users installing the latest Chrome version, which can take weeks or months.
Unnamed Update — July 21, 2018
Algorithm trackers and webmaster chatter signaled heavy rankings flux, but Google did not confirm. MozCast recorded its highest temperature in 2018 at 114°F.
Mobile Speed Update — July 9, 2018
Six months after announcing it, Google rolled out the mobile page speed update, making page speed a ranking factor for mobile results. Google claimed that this only affected the slowest mobile sites, and there was no evidence of major mobile rankings shifts.
Video Carousels — June 14, 2018
Google moved videos from organic-like results with thumbnails into a dedicated video carousel, causing a shake-up in results that were previously tracked as organic. At the same time, the number of SERPs with videos increased significantly (+60% in MozCast).
Unnamed Update May 23, 2018
Algorithm tracking tools and webmaster chatter showed heavy activity, but Google did not confirm an update. MozCast showed very high temperatures over a 3-day period, peaking on May 23.
Snippet Length Drop May 13, 2018
After testing longer display snippets of up to 300+ characters for a few months, Google rolled back most snippets to the former limit (about 150-160 characters).
Unnamed Core Update April 17, 2018
MozCast picked up heavy algorithm flux that peaked on April 17 and continued for over a week. Google later confirmed a "core" update, but didn't provide any specifics and the update wasn't named by Google or the SEO community.
Mobile-First Index Roll-out — March 26, 2018
Google announced that the mobile-first index was finally "rolling out." Since the index has been in testing for many months, and Google has suggested they are migrating sites gradually, it's unclear how much impact this specific roll-out had on the overall index. Webmaster should begin to see notifications within Google Search Console.
Zero-result SERP Test — March 14, 2018
On a small set of Knowledge Cards, including some time/date queries and unit conversion calculators, Google started displaying zero organic results and a "Show all results" button. A week later, Google stopped this test, but we believe it is an important sign of things to come.
"Brackets" Core Update — March 8, 2018
Google confirmed a "core" update on March 7th, but volatility spiked as early as March 4th, with a second spike on March 8th, and continued for almost two weeks. This may have been multiple updates or one prolonged, rolling update. The "Brackets" name was coined by Glenn Gabe; no details were provided by Google.
Unnamed Update — February 20, 2018
Rankings showed a spike in volatility (across a number of tools) around February 20th, which quickly settled down, sometimes signalling a targeted algorithm update. Google did not confirm any update in this time period.
Resource:- Google Update